How to Avoid Getting "Cannot read property of undefined" in JavaScript
One of the most common type errors in JavaScript is the famous "Cannot read property of undefined". This error occurs when you try to read or access a property on an object that is undefined. Another common case that is caused by a similar issue, is when you get the same error message, but with null instead of undefined.
Cannot read property of null
Why does this happen?
Imagine the following situation. You have a user object that is initially undefined, and it is populated through a fetch request. Your server is down and so it returns with an undefined value, but you didn't handle this failure path, and you still try to read properties from the user object:
let user; // The variable is set to undefined
user = await getUser(id); // The request fails and returns `undefined`, but it is not handled
console.log(user.name); // You try to log the `name` property of the `user` object, that is still `undefined`The variable in the code example above is declared, but its value is still set to undefined. Here you are essentially trying to do the following:
console.log(undefined.name); // This will throw "Cannot read property 'name' of undefined"
// Same as if the request returns with a `null` and you try to read properties from that
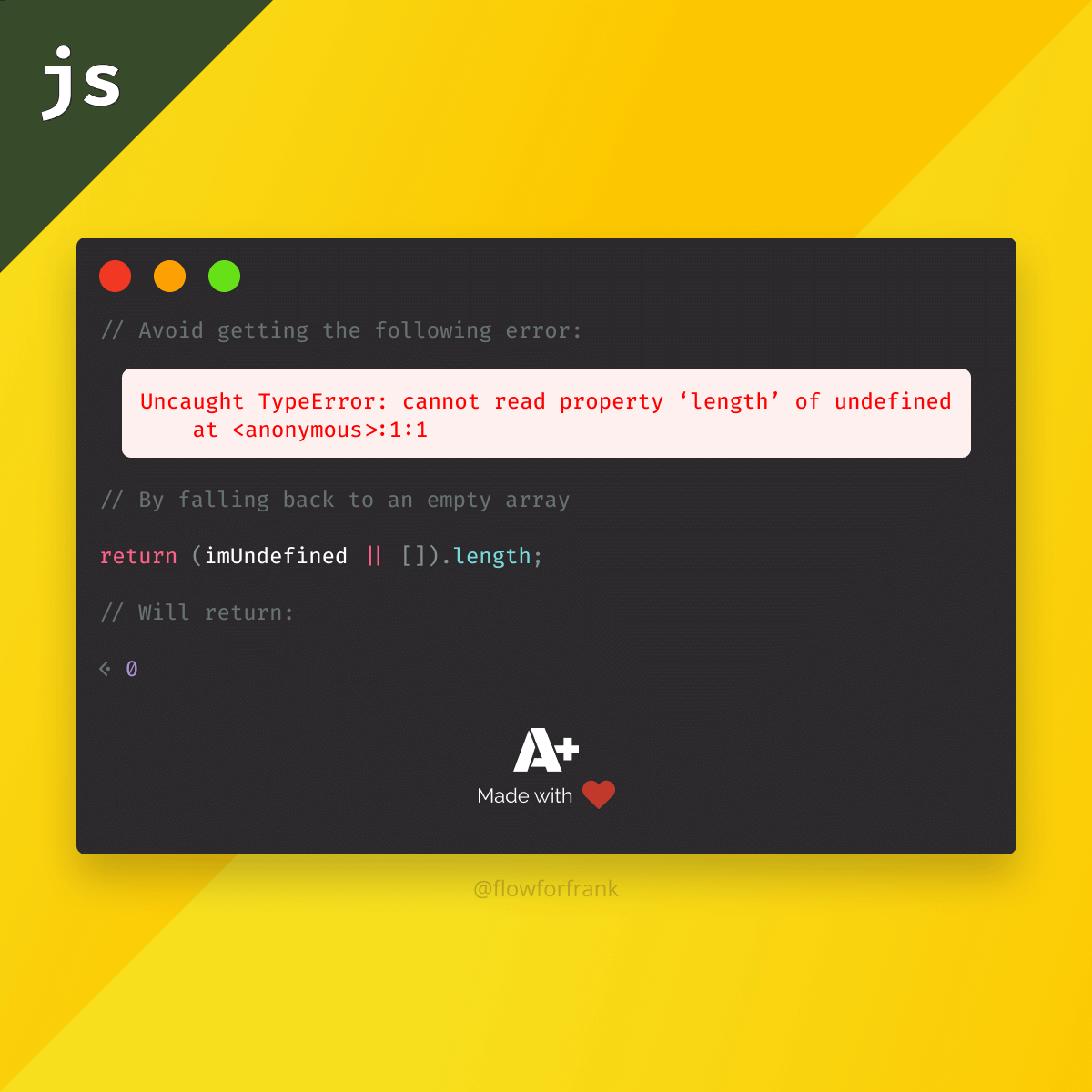
console.log(null.name); // This will throw "Cannot read property 'name' of null"Since undefined is not an object, you will get a TypeError, like the one below. So how can we avoid this?

Avoiding errors
To avoid getting these types of errors, we need to make sure that the variables we are trying to read do have the correct value. This can be done in various ways. We can do if checks before dealing with objects whose values are bound to change:
if (user !== undefined) {
// Here `user` is surely not `undefined`
}
if (typeof(user) !== 'undefined') {
// We can also use the `typeof` operator
}A much cleaner solution however is to use the logical OR operator, when you assign a value to a variable, or even better, when you return the value from the function:
// Assign a fallback during declaration
user = getUser(id) || {};
// Assign a fallback during return
const getUser = id => {
...
return userResponse || {};
};If getUser returns undefined or null, then we can fall back to an empty object, and assign that to the user variable. This way, if we try to access user.name, we will get undefined, as we don't have that property on the user object, but we still have an object to work with, so we don't get an error. We can also use TypeScript to easily spot these types of mistakes right inside our IDE.

Resources:

Rocket Launch Your Career
Speed up your learning progress with our mentorship program. Join as a mentee to unlock the full potential of Webtips and get a personalized learning experience by experts to master the following frontend technologies: