What is the Difference Between A URL And A URI?
As a developer, you’ve already heard about URL countless times. You may have also come across URI before and now you want to know what is the difference between the two if there’s any. They are often used interchangeably but we have to differentiate between the two. Before doing a comparison, let’s see what each of them means by definition.
What is a URL?
A Uniform Resource Locator or URL for short — as the name suggests — is a reference for a resource and a way to access that resource. It is often referred to as the address of a website. The one you find in your address bar.
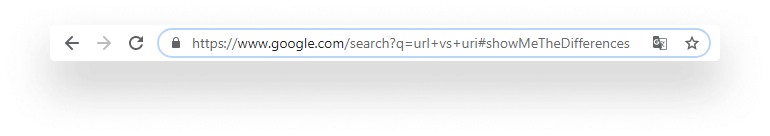
A URL is made up of a couple of different parts:
- A protocol: Usually
httpsorhttp. A way to tell how to access the resource. You may have also seen other commonly used protocols suchftp, orfile. - This is followed by
:// - A hostname: A registered name — or an IP address — that represents an IP address — a numeric identifier that is used for identifying a device connected to a network.
- Followed by an optional port that is preceded by a colon.
- A path: It can refer to a file system path, but is also often used as a slug.
- Optional query parameters that are preceded by a question mark, and where multiple parameters are concatenated with an ampersand
- Lastly, an optional fragment preceded by a hash. It is used for providing quick links for headings on a page.
To demonstrate it through the above image, this is how the URL would look like in a diagram:

What is a URI?
Now that you fully understand how a URL is made up, let’s see what exactly is a URI. Just like a URL, a Uniform Resource Identifier also provides a way to identify resources. But unlike URLs, they don’t necessarily provide the means to locate said resources.
An example for a URI — that is not a URL — is an ISBN number that is used for identifying books. It clearly identifies the resource with a unique number, but it does not provide any means to actually reach the resource.
Therefore, we can conclude that a URI is a superset of URLs and that each URL is essentially a URI as well.

The Difference Illustrated
To illustrate how they are connected, take a look at the following Venn diagram:
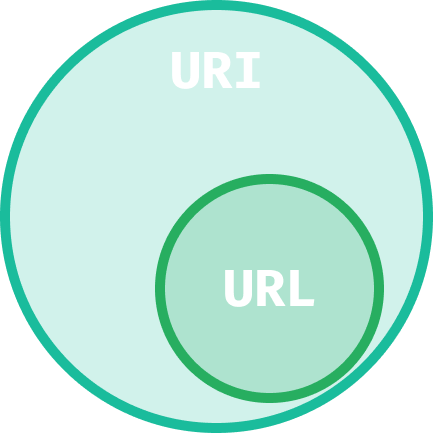
Really a URL is a type of URI, that also includes information on how to access a resource. If there’s only one thing to take from this tutorial, be it this one sentence from RFC3986:
The term “Uniform Resource Locator” (URL) refers to the subset of URIs that, in addition to identifying a resource, provide a means of locating the resource by describing its primary access mechanism.
Summary
As web developers, we have to memorize lots of acronyms and initialisms. The deeper you understand core concepts about how the internet works, the easier you can do your job, the higher the quality of your work will be, and the more knowledgeable you will become.
With this tutorial, now you also know the difference between URI and URL. If you still have any doubts in your head, don’t hesitate to ask questions in the comments section. Thank you for reading through, happy coding!

Rocket Launch Your Career
Speed up your learning progress with our mentorship program. Join as a mentee to unlock the full potential of Webtips and get a personalized learning experience by experts to master the following frontend technologies: