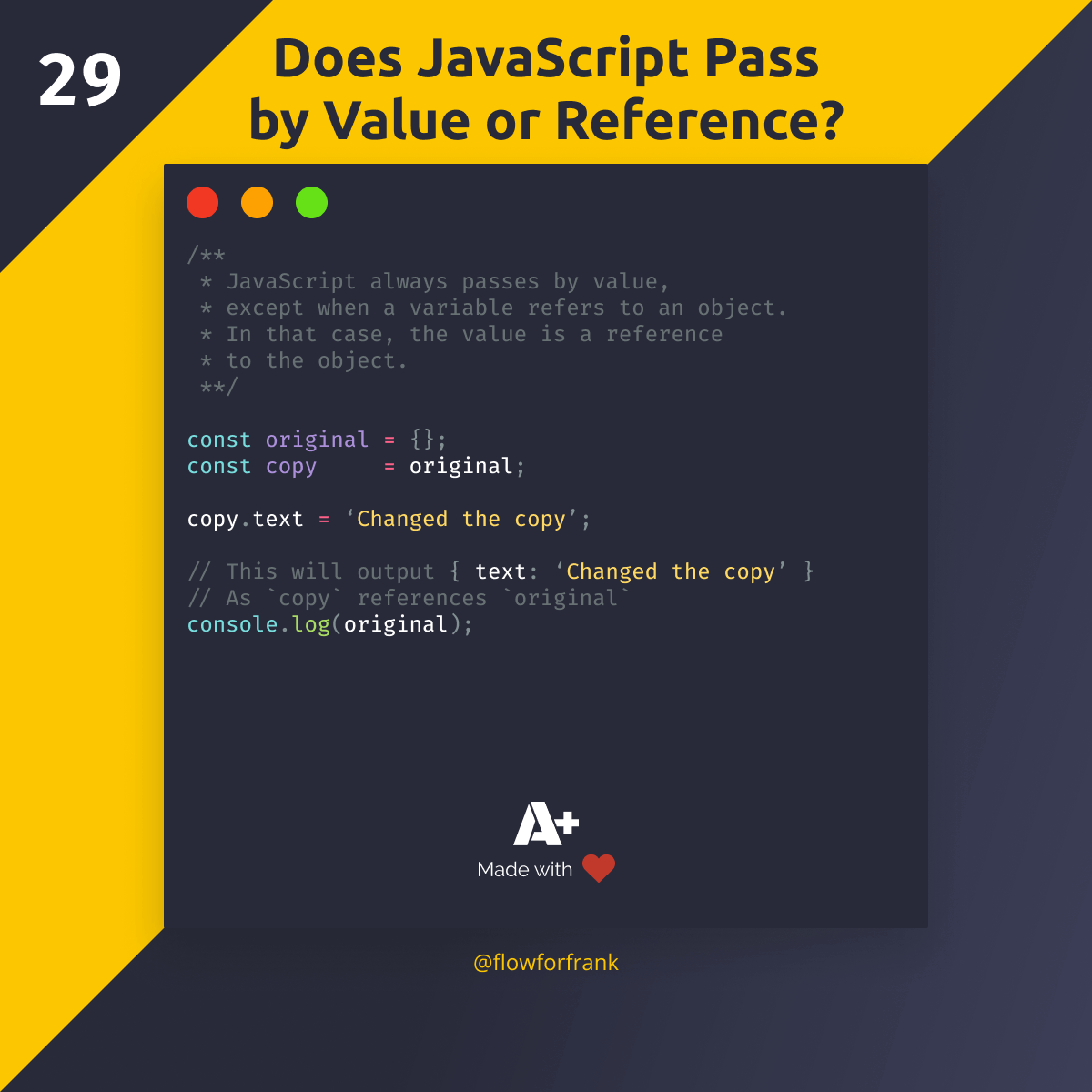
Does JavaScript Pass by Value or Reference?
JavaScript always passes by value, except when a variable refers to an object. In that case, the value is a reference to the object.
Copied to clipboard! Playground
const original = {};
const copy = original;
copy.text = 'Changed the copy';
// This will output { text: ‘Changed the copy’ }
// As `copy` references `original`
console.log(original);You can try it out with the example above. Even though you've changed copy, as the reference is pointing to original, it will be changed too. In order to do deep copy an object — meaning you also create a new reference to detach from the original — you can use one of the examples below:
Copied to clipboard! Playground
// Using JSON.parse & JSON.stringify
JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj));
// Using Object.assign
Object.assign({}, obj);
// Using object spread
{ ...obj };
📚 More Webtips
Master the Art of Frontend
Access 100+ interactive lessons
Unlimited access to hundreds of tutorials
Prepare for technical interviews